ANTIBODY
Also known as IMMUNOGLOBIN(Ig). The antibody is denoted by "Ab".
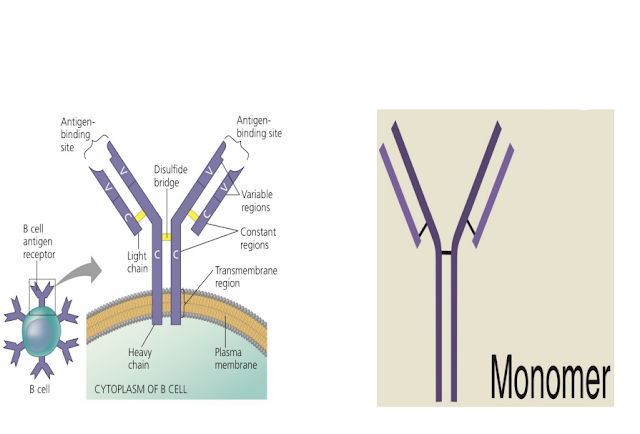
The antibody is a complex glycoprotein molecule, secreted by plasma B
lymphocytes. Each antibody molecule has four polypeptide chains, two small
called light chains and two longer called heavy chains, held together
by interchain disulfide bonds in the shape of Y. It is represented as H2L2. One heavy chain and one light chain are called dimers. In antibody, there is a site of recognition is known as the Antigen binding site also known as the Antigen binding site or Paratop.
 |
| License to NCERT |
Different classes of Antibodies
- Different types (classes) of antibodies are produced in our body: IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, and IgE.
IgG Antibody
- Most abundant antibody.
- About 75% of total antibodies are in the blood.
- Can cross the placenta(smallest).
- Provides natural passive acquired immunity to the fetus.
- Two paratop is present.
- Second most abundant (about 10%)
- Dimer antibody
- Secretory antibody means present in secretion such as saliva and tears.
- Present in saliva, tears, sweat, mucus
- Protects mucosal lining (inhaled pathogen)
- Also present in colostrum (Natural passive acquired immunity to infants).
- Four paratop is present.
IgD Antibody
- Fixed or surface antibody.
- Acts as a B cell receptor (BCR) means activating B cells.
- Two paratop is present.
IgE Antibody
- Present in very small quantity (0.05%).
- Involved in type 1 hypersensitivity (allergy).
- Stimulates mast cells and basophils.
- Also protects from parasitic infections (Helminthic).
- Two paratop is present.
IgM Antibody
- Pentamer antibody
- Largest antibody
- Millionaire or heaviest antibody (M.W. = 9,60,000)
- Oldest antibody
- The first antibody formed by the fetus by the age of 5 months against congenital infections(Intrauterine infection).
- Ten paratop is present.
NOTE:-
- For acute infection(severe)⟶ IgM
- For chronic infection(long-lasting)⟶ IgG
The functions of antibodies are agglutination, opsonization, and
neutralization.
Agglutination
An antibody is attached with the antigen, present on the surface of the pathogen, and in turn, destroy the pathogen by cell lysis.
Opsonisation
Coating of bacteria (Ag) with
opsonin antibody (IgG and
IgM) facilitates the
phagocytes cells and these
antibodies or opsonins
promote phagocytosis by
combination with antigen.
Neutralization
Antibodies neutralize the toxin of bacteria by attaching it with them.








0 Comments
Post a Comment
If you have any doubt, please let me Know